Appendix B: Determination of Need for Traffic Control at School Crossings
Anchor: #i999214Introduction
The determination of need for traffic control at a school crossing involves a five step process. This appendix explains the five steps and provides example data and calculations for a hypothetical crossing.
The Pedestrian Group Size Study form and the Pedestrian Delay Time Study form provide a means of documenting the process (See Appendix A). Districts may also create their own forms for this purpose.
Be sure that the basic information concerning the time of the study and the location is recorded on the forms.
EXAMPLE:
Figure B-1. Example basic information concerning time and location of study
Anchor: #i999249Step 1. Pedestrian Count
Pedestrian counts should be made on a normal school day during the heaviest hours of crossing activity in the morning or afternoon — preferably both. A tabulation should be made of the number of children crossing the roadway and the time required for the group to cross. It is assumed that up to five pedestrians will walk abreast when a group crosses the roadway. The number of rows is determined by dividing the group size by five. Note that the number of rows is taken as a whole number, since even one pedestrian in excess of an even five will make an additional row, requiring extra clearance time.
EXAMPLE:
Figure B-2. Example pedestrian count
Anchor: #i999274Step 2. Determination of the Number of Rows N
The total number of groups is found by adding up the number of groups that crossed the roadway. This number is then multiplied by 0.85 to obtain the 85 percentile cumulative number of groups (C). C is then compared to the CUMULATIVE column, where the cutoff point is chosen. The CUMULATIVE column cutoff point is the first number greater than or equal to C, as read from the bottom to the top in the column. At the cutoff point the 85 percentile number of rows N can be found in the NUMBER OF ROWS column.
EXAMPLE:
Figure B-3. 3. Example determination of the number of rows N
Anchor: #GRIIEKJHStep 3. Determination of the Adequate Gap Time G
The adequate gap time G is determined from the equation:
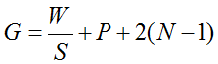
Where:
- Anchor: #NRSKTBKD
-
W is the curb-to-curb road width in feet.
Anchor: #EYCJSMKL -
N is the 85 percentile number of rows.
Anchor: #TWLOUFCT -
S is the average walking speed — assumed to be 3.5 ft./sec.
Anchor: #OMCXNNEF -
P is the average perception and reaction time — assumed to be 3.0 seconds
Anchor: #HSXTVRQV -
2(N –1) is the pedestrian clearance time.
EXAMPLE:
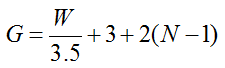
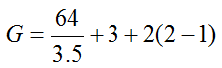
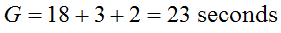
Step 4. Pedestrian Delay Time D
Pedestrian delay time is determined by recording the number of gaps with a gap size greater than or equal to the adequate gap time G. (The Pedestrian Delay Time Study form is designed for this purpose.) The number of gaps for a particular gap size is then multiplied by the gap size. Then the total time t of all gaps equal to or greater than G is found by adding up the product of the number of gaps and the gap size. The actual pedestrian delay time D is then found by the equation:
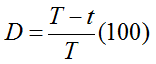
Where T is the total survey time in seconds.
EXAMPLE:
Figure B-4. Example determination of pedestrian delay time D
Anchor: #i999383Step 5. Determination of Need for Traffic Control
Curb-to-curb width (W), pedestrian delay time (D), and the 85 percentile number of rows (N) can be plotted on a graph as shown in Figure B-5 to determine if control is needed.
EXAMPLE: The graph shown in Figure B-5 shows that a traffic signal could be justified in the hypothetical example, since point A is above the line N=2.
Figure B-5. Determination of need for traffic control at school crossings. Here a traffic signal could be justified, since point A is above the line N=2.