Section 2: Guide Sign Components
Anchor: #i1003403Introduction
Directional information on conventional highways is provided primarily through the use of highway class, highway number, and cardinal directions. Destination information (city names) may also be provided, but this information is of secondary emphasis.
Conventional guide signs consist of assemblies and stand-alone signs. Assemblies are created by combining several different signing components in a single sign installation. Stand-alone signs are a single sign and are described in more detail in Section 5 (page 3-36).
The typical single assembly consists of, from top to bottom, a cardinal direction sign, a route sign, and a directional arrow sign. Single assemblies may be combined at one sign installation so that there could be various combinations of cardinal direction signs, route signs, and arrow signs.
There are also other types of signs that are sometimes used in assemblies.
This section describes the different types of components that can be used in a conventional guide sign assembly. Table 3-1 identifies the guide signs that are used to provide directional information and the general purpose for each of these types of signs. The table also identifies the figures that illustrate the appearance of each type of sign. Specific uses and applications of these signs are described and illustrated in the remaining subsections.
The arrangement of these components within an assembly is described in Section 3, and the different types of assemblies are described in Section 4.
|
Location in Assembly |
Type of Guide Sign |
General Purpose |
Illustrated in: |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Above Route Sign |
Cardinal Direction Signs |
Provide a general indication of the direction of travel of the highway over its full length. |
Figure 3-6 |
|
Junction Signs |
Provide advance notice of the intersection of two or more highways. |
Figure 3-4, 3-5 |
|
|
Auxiliary Signs |
Indicate various information about a highway. |
Figure 3-14 |
|
|
Route Sign |
Route Signs |
Indicate the class and number of a particular highway. |
Figure 3-2, 3-3 |
|
Below Route Sign |
Arrow Signs |
Indicate turning information at the intersection of two or more highways. |
Figure 3-9, 3-10, 3-11, 3-12 |
|
Lane Use Signs |
Indicate the proper lane position to travel to the indicated highway. |
Figure 3-13 |
Anchor: #i1003442
Route Signs (Texas MUTCD 2D.10 and 2D.11)
Purpose: Route signs identify the class and number of the highway of interest.
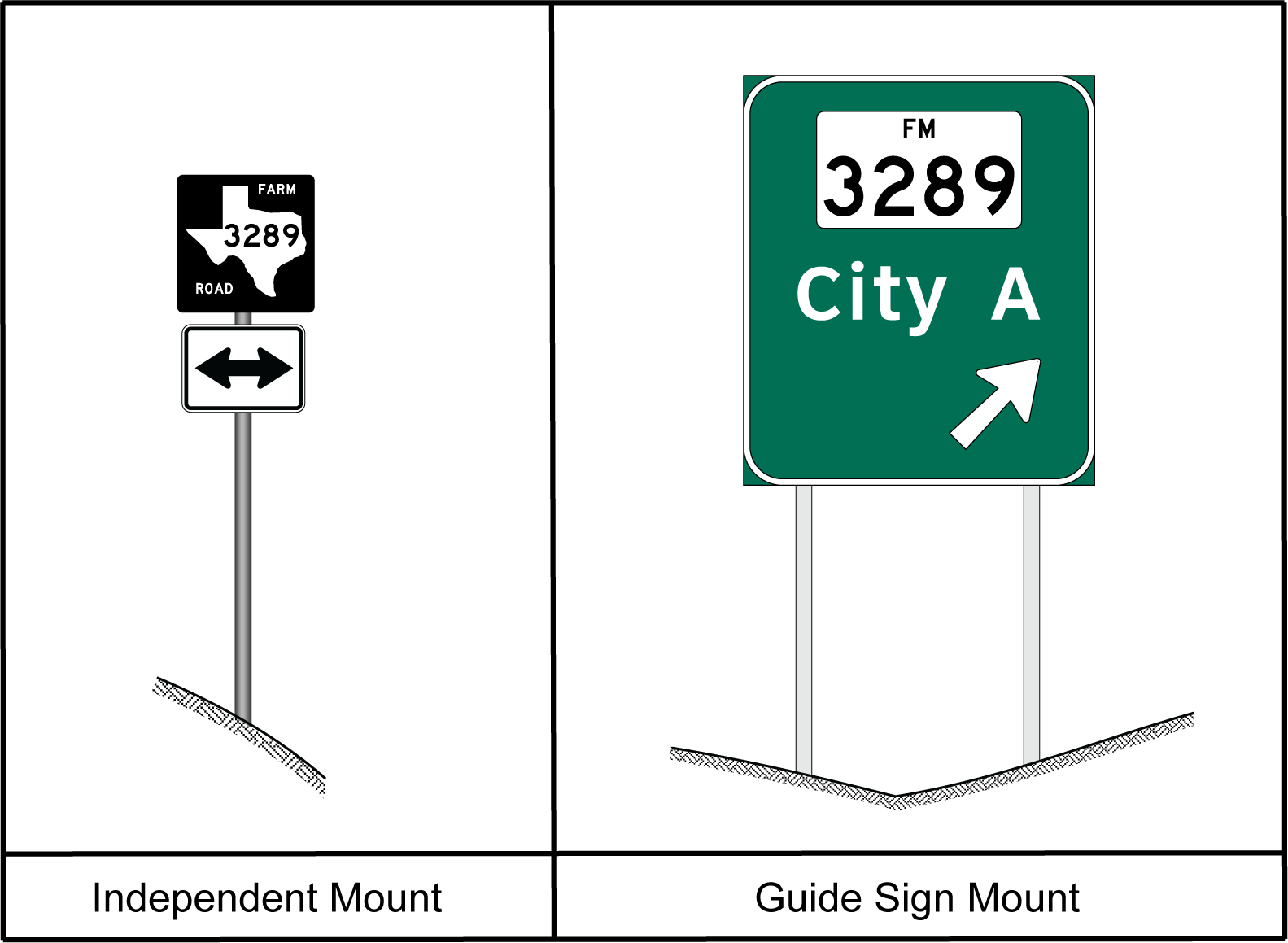
Route signs can be divided into two different groups, independent mount and guide sign mount, depending upon the manner in which they are mounted. Figure 3-1 illustrates the differences between the two types of route sign mounts, and the differences are described below.
- Anchor: #CUQLXKSS
- Independent Mount - Route signs that are mounted directly to a post. Figure 3-2 shows the appearance of independently mounted route signs. Anchor: #IYDOIKAS
- Guide Sign Mount - Route signs that are attached to a larger guide sign. Figure 3-3 shows the appearance of guide sign mounted route signs.
As a general rule, independent route signs should not be mounted within a guide sign, and guide sign route signs should not be mounted on a post.
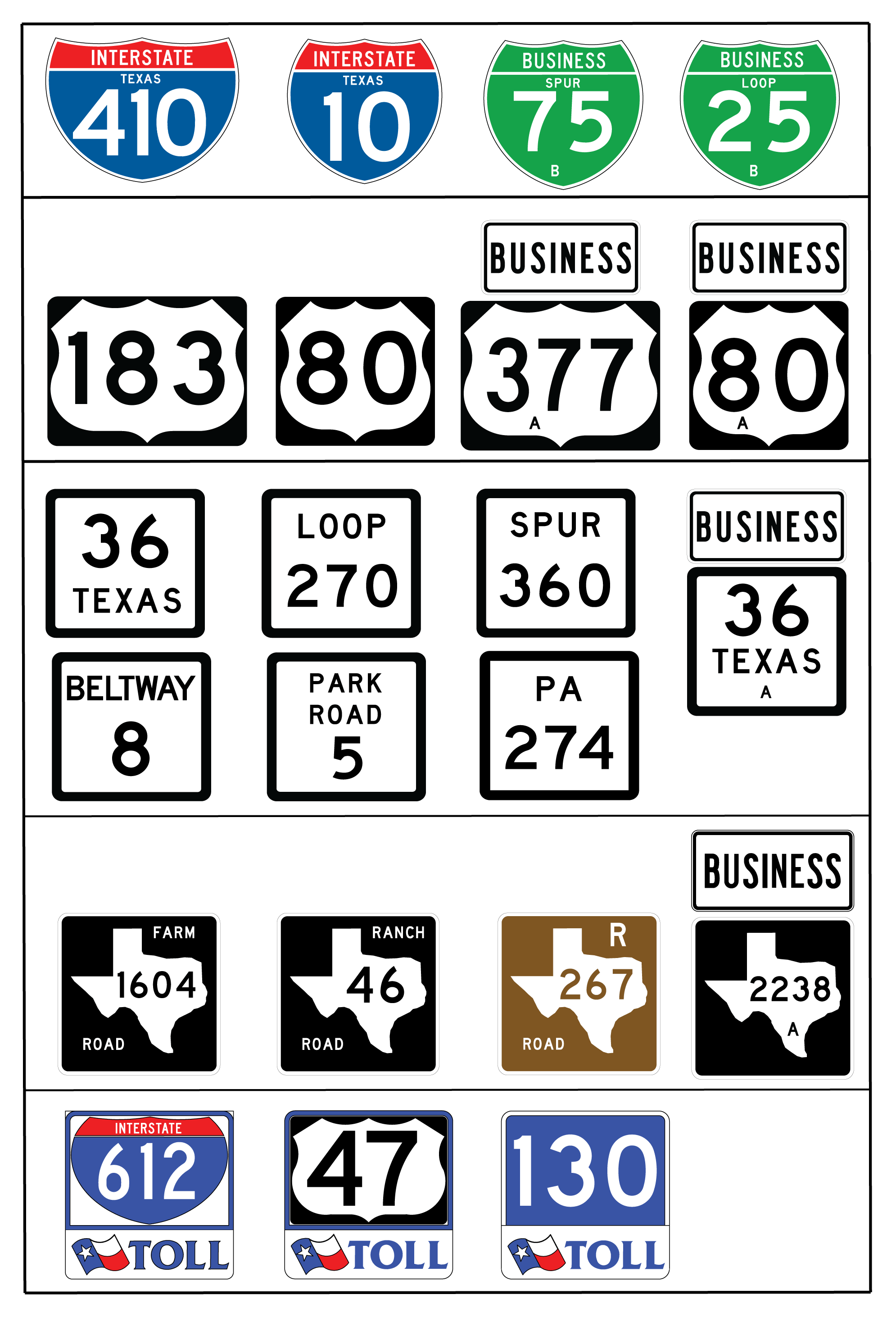
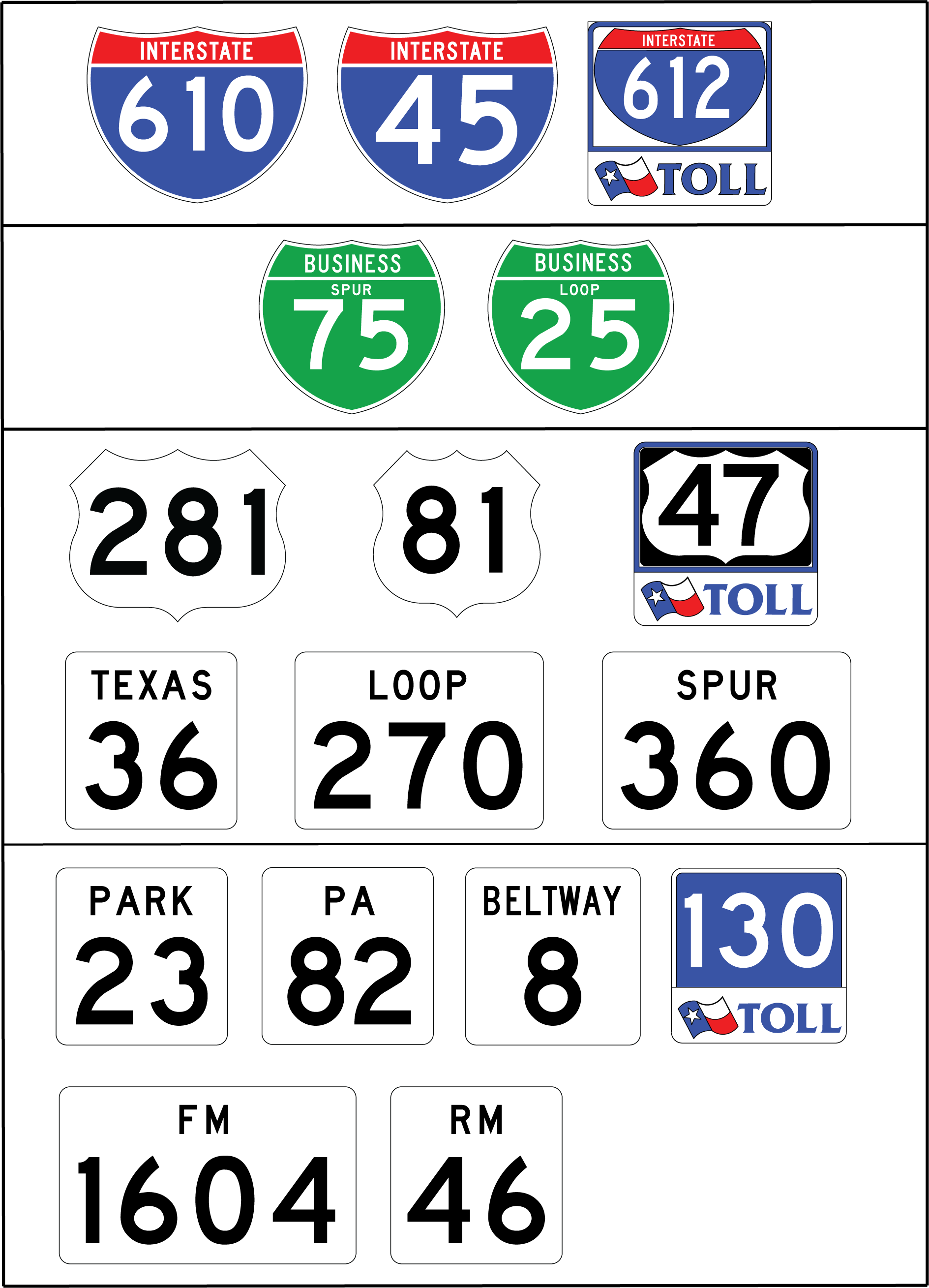
Route signs of each group can also be divided by the highway classification. They use five basic types of independent route signs: Interstate shield, U.S. Highway shield, State Highway shield, Farm/Ranch to Market Road shield, and toll road shields. For guide sign mount route signs, the State Highway and Farm/Ranch to Market Road shields have similar appearances.
Information about the hierarchy of route signs is provided in Section 3 (page 3-17).
Figure 3-1. Types of Route Sign Mounts
Figure 3-2. Route Signs for Independent Mounting
Figure 3-3. Route Signs for Guide Sign Mounting
Special notes for route signs:
- Anchor: #FLCXSMRT
- Business Auxiliary Sign: A Business sign (M4-3) should be displayed with the route sign in an independent mount to indicate a business route. Anchor: #XPLDYPLU
- Letter below route number in Business Routes: All business route signs have a letter below the number in the route shield. This number allows TxDOT to distinguish between business highways in different cities that are off the same major highway. For example, there is a U.S. Highway Business 77 in Robstown (77U), another U.S. Highway Business 77 in Kingsville (77V), and still another in Raymondville (77W). The letter provides an administrative distinction between business highways and is not intended for drivers. Therefore, it is a small letter on the sign. The four business route signs in Figure 3-2 have an “A” below the highway number illustrating this application.
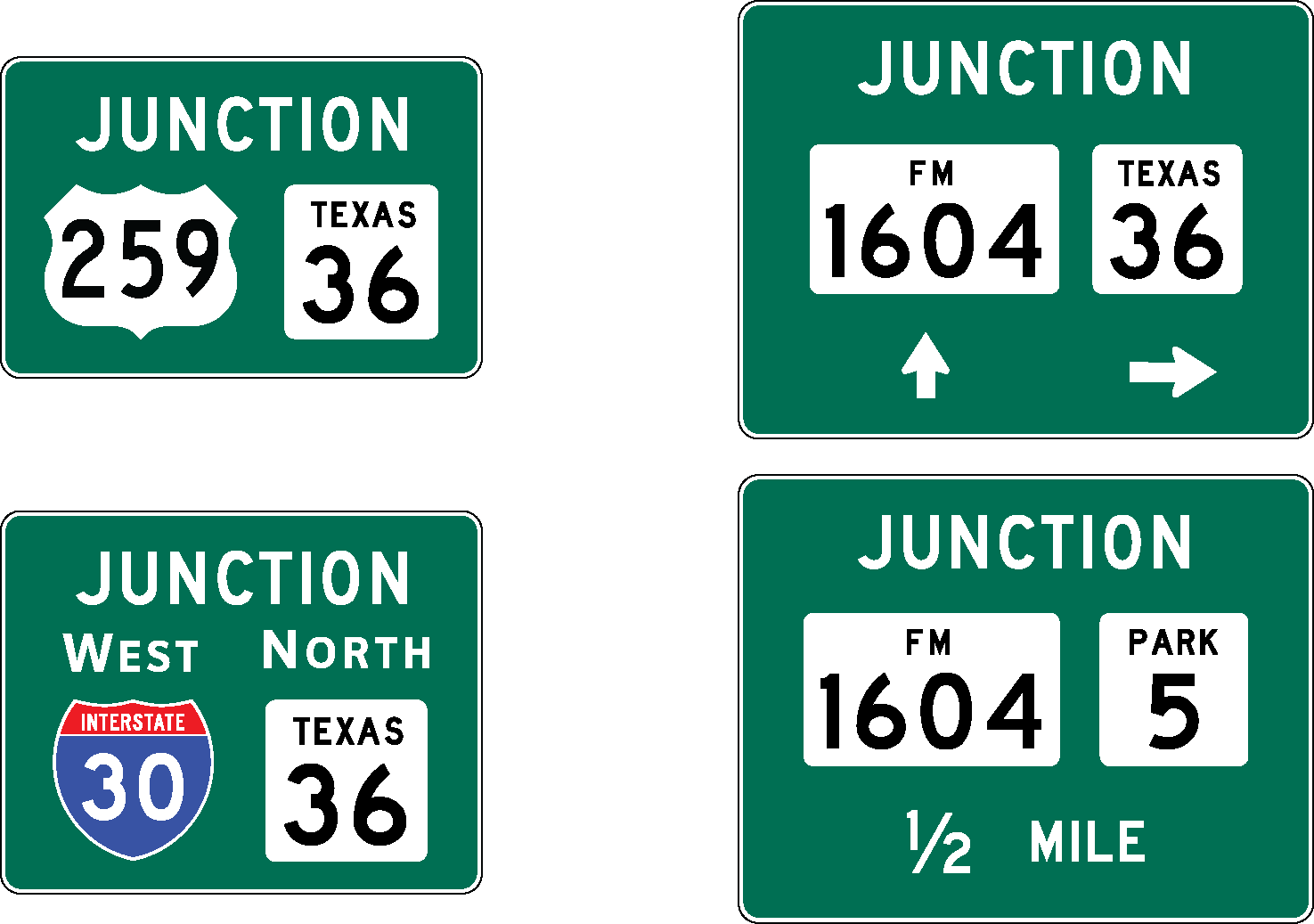
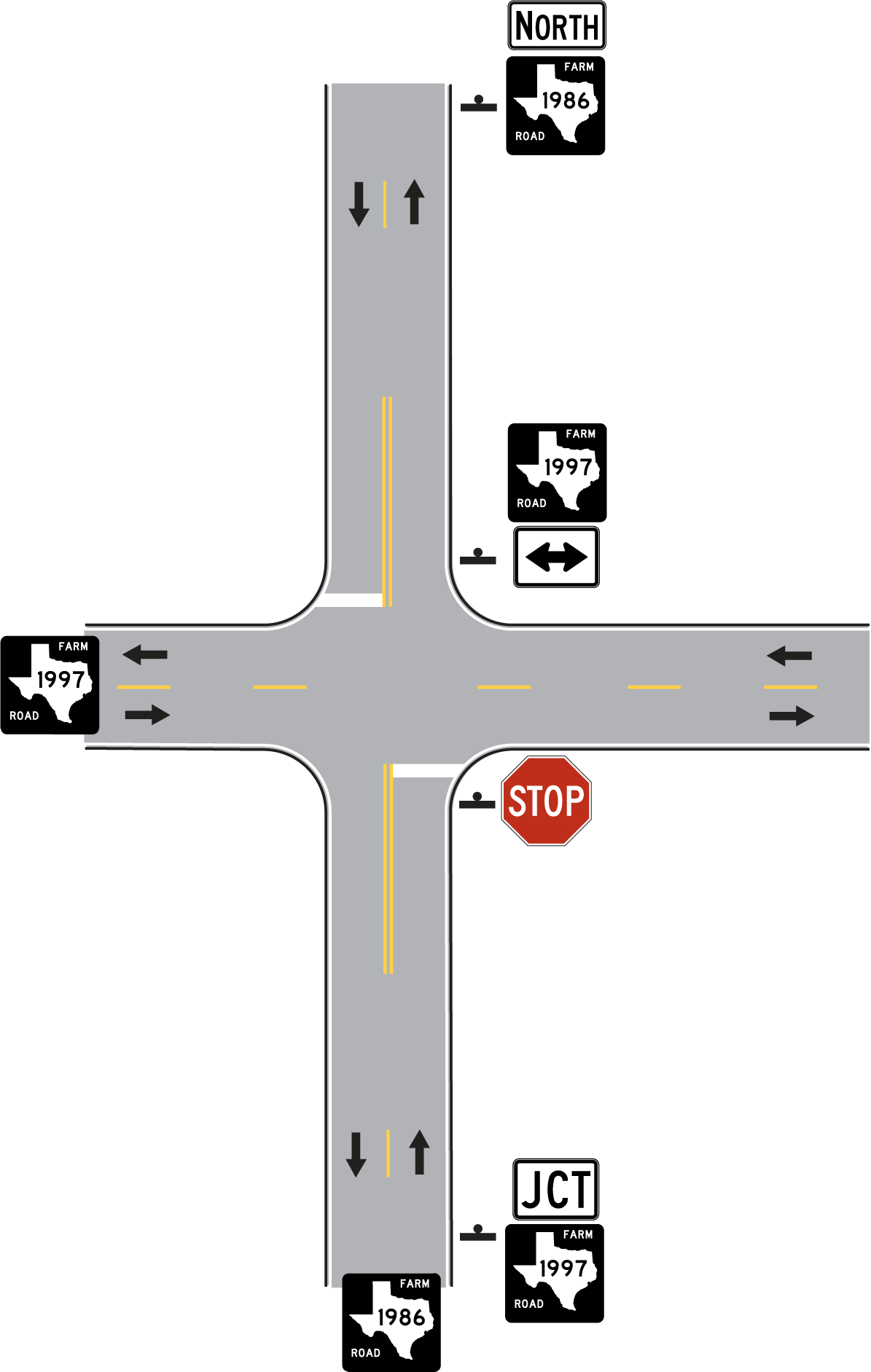
Junction Sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.13 and 2D.14)
Purpose: Junction signs provide advance notice of an intersection with the indicated highway(s).
There are two different methods of indicating a junction:
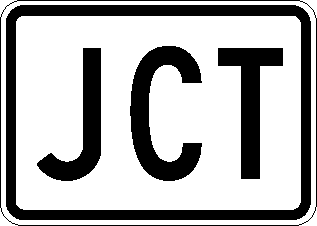
- Anchor: #JRGJKMJD
- Junction Auxiliary Sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.13): Most junctions are indicated with the JCT sign, as shown in Figure 3-4. The Junction sign is mounted at the top of an assembly, either directly above the route sign or above an auxiliary sign (such as BUSINESS or ALT). Anchor: #OYHKOVHC
- Combination Junction Sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.14): Some junctions may require the use of a combination junction sign, as shown in Figure 3-5. The combination sign contains the word JUNCTION at the top of the sign and the appropriate route signs below. Other information may also be included in the combination sign, such as the cardinal direction, arrows, destination cities, and distance to the junction.
Where shields are used in a Combination Junction sign, they shall mimic the shields used on large ground mounted guide signs (route signs for guide sign mounting).
The Junction Assembly subsection (page 3-28) contains additional information about junction signing and provides additional examples of junction signing.
Figure 3-4. Junction Sign (M2-1)
Figure 3-5. Combination Junction Sign (M2-2)
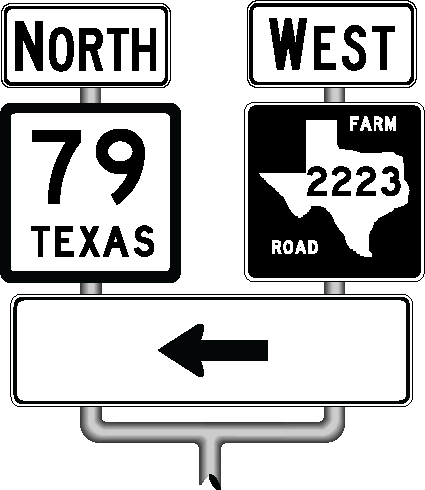
Anchor: #i1003582Cardinal Direction Auxiliary Signs (Texas MUTCD 2D.15)
Purpose: Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs indicate the general direction of a route. A Cardinal Direction auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign(s) to which it applies. Figure 3-6 illustrates Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs.
Special Notes for Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs:
- Anchor: #WXQBLIBX
- A Cardinal Direction sign should be used with a route sign except in a Reference Marker assembly. Anchor: #NHLYEHVJ
- Cardinal Direction auxiliary signs use the larger initial letter design shown in the Texas MUTCD as shown in Figure 3-6. Anchor: #IXMOTMXT
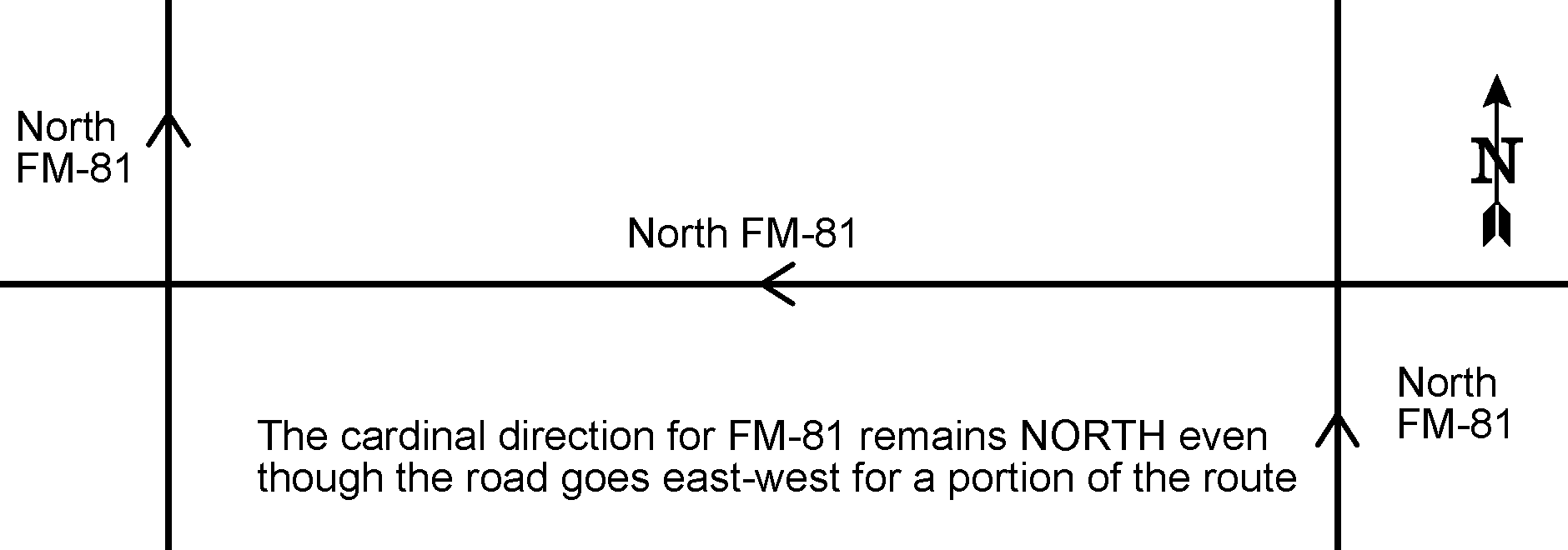
- The cardinal direction shown in the auxiliary
sign may be different from the actual compass direction of travel
on that direction. Each highway has a designated cardinal direction
for the highway. For consistency purposes, the cardinal direction
for someone traveling on a route should be the same throughout the
length on one direction of the highway. Figure 3-7 illustrates how
a cardinal direction should remain the same on a highway regardless
of the compass direction of travel. Cardinal directions for state
routes are established by the Texas Transportation Commission at
the time of its original designation. Contact TxDOT’s Transportation Planning
and Programming Division to determine the official cardinal direction
for any route.
- Anchor: #MYEMHXOU
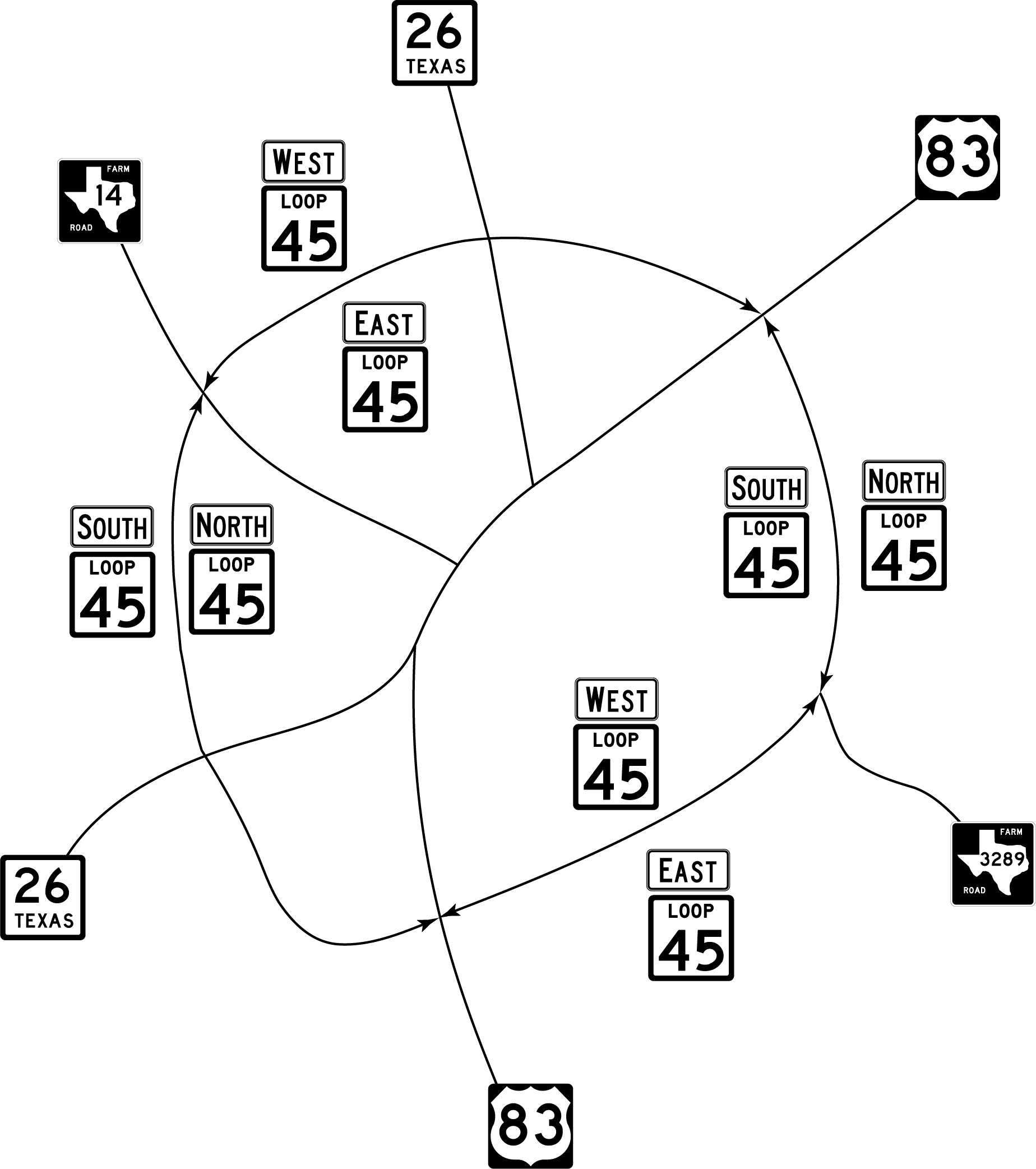
- For Interstate and U.S. Highways, even-numbered routes have east-west cardinal directions, and odd-numbered routes have north-south cardinal directions unless the highway is a loop. A loop may use multiple cardinal directions as indicated in Figure 3-8. Anchor: #EKDXIIWS
- For all other classes of highways, there is no relationship between the cardinal direction and the route number.
Anchor: #VOGNPUDH - For highways not on the Interstate or U.S. Highway system, the cardinal direction is based on the greatest north-south or east-west distance between the start and end point of the highway. If the straight-line east-west distance between the starting and ending point of a highway (statewide, not just in the district) is greater than the straight-line north-south distance, then the cardinal direction should be east-west for the complete length of the highway throughout the state. Anchor: #TYXQBJDB
- For a loop highway, for which there is no starting or ending point, the cardinal direction changes to be generally consistent with the compass direction. The changes in cardinal direction should occur at interchanges or intersections. Figure 3-8 illustrates an example of cardinal directions for a loop highway.
Figure 3-6. Cardinal Direction Signs
Figure 3-7. Relation between Cardinal Direction and Compass Direction
Figure 3-8. Assigning Cardinal Direction to a Non-Interstate Loop Route
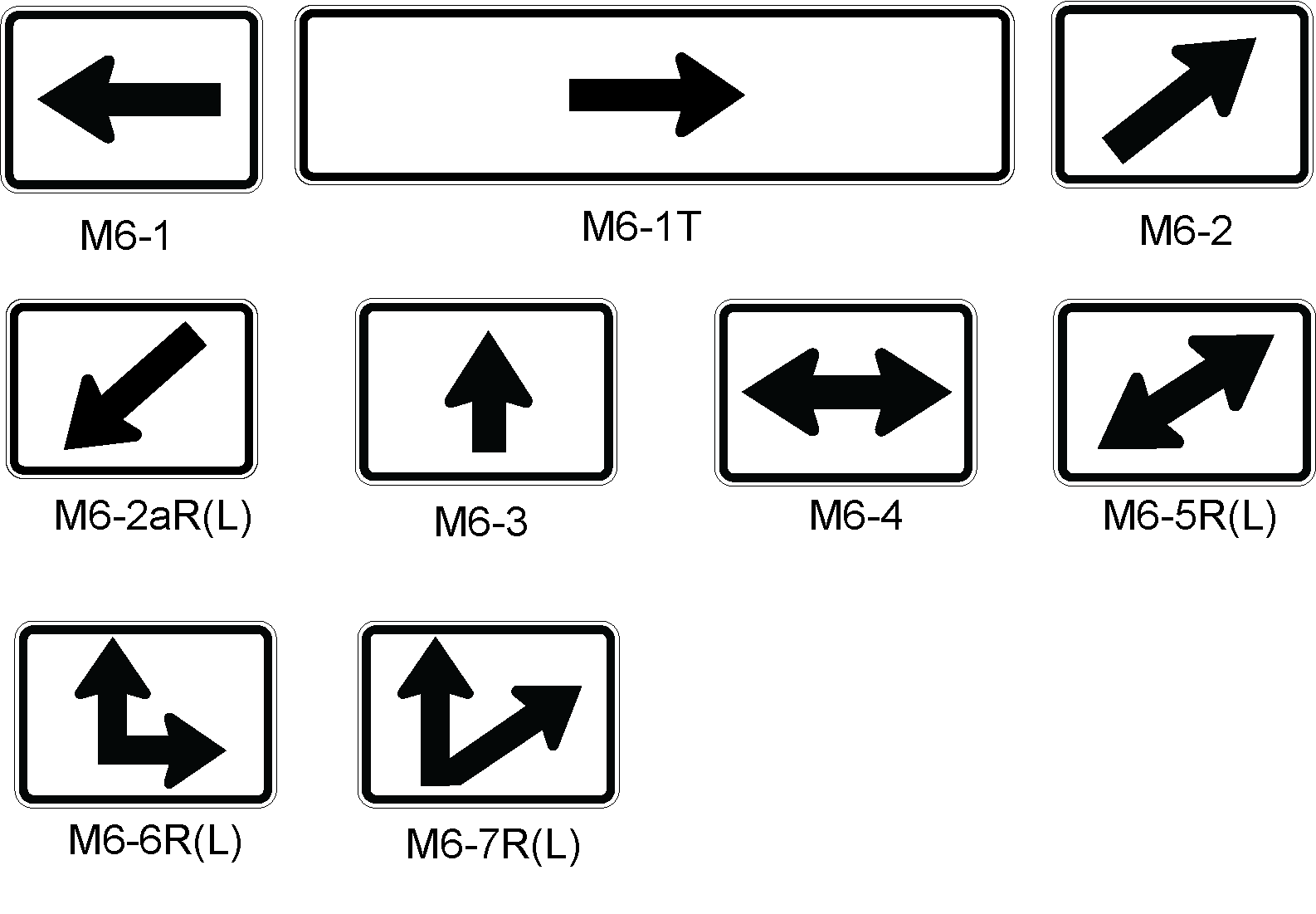
Anchor: #i1003663Arrow Signs (Texas MUTCD 2D.26 and 2D.28)
Purpose: Arrow signs indicate the direction of turn necessary to travel on the indicated highway in the indicated cardinal direction. An Arrow sign is mounted below the route sign(s) to which it applies. There are two types of arrow signs: Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary sign and Directional Arrow auxiliary sign.
- Anchor: #PLDGYJBT
- Advance Turn Arrow Auxiliary Signs
(Texas MUTCD 2D.26)
-
Anchor: #MJMGKPRM
- Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary signs are used in the Advanced Route Turn Assembly (see page 3-29) to indicate that the route the driver is currently on turns at the highway intersection. This typically occurs where two concurrent (overlapping) highways split, and the driver is required to turn to stay on one of the highways. Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary signs are used only in an Advance Route Turn Assembly (see page 3-29). Examples of Advance Turn Arrow auxiliary signs are shown in Figure 3-9. Anchor: #GORHJUIF
- The Texas MUTCD requires (a shall condition) the Advanced Route Turn Assembly to be used when a turn must be made to remain on the indicated highway. The Advance Route Turn Assembly is described in more detail on page 3-29.
Anchor: #UCJJEOHR - Directional Arrow Auxiliary Signs (Texas
MUTCD 2D.28)
-
Anchor: #RXKUKMDJ
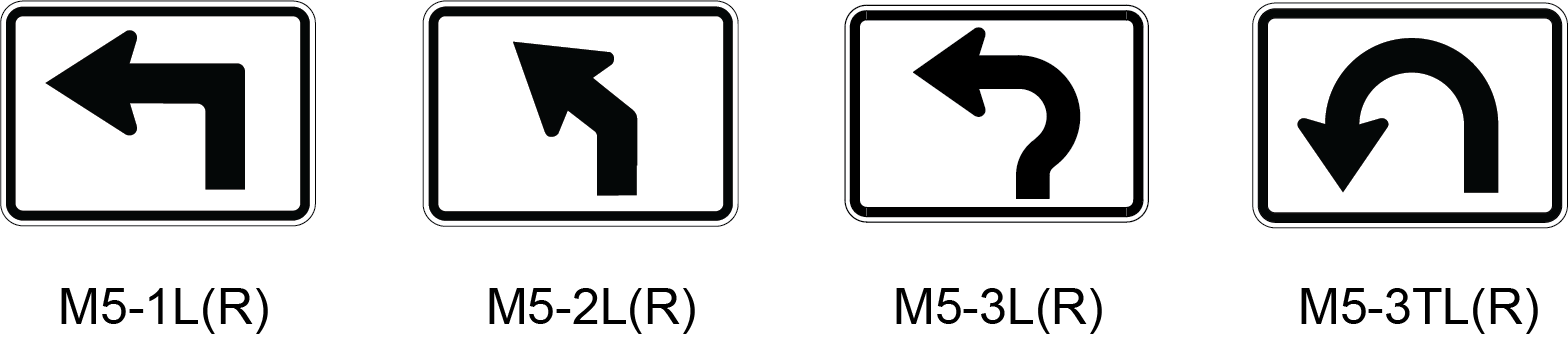
- Directional Arrow auxiliary signs are used to indicate the direction that a driver must follow to travel on the indicated route. Directional Arrow auxiliary signs are typically used only in Directional Assemblies, although similar type arrows are also used as a component in Destination and Combination stand-alone signs. The sign can display either a single- or double-headed arrow, as shown in Figure 3-10. The use of Directional Arrow auxiliary signs in a Directional Assembly is described on page 3-31.
Figure 3-9. Advance Turn Arrow Auxiliary Signs
Figure 3-10. Directional Arrow Auxiliary Signs
Anchor: #i1003723Double Arrow Sign
The double-headed arrow sign (M6-4), shown in Figure 3-10, is to be used in directional assemblies at intersections when all of the following conditions are met:
- Anchor: #JRHFYJRA
- Intersection is rural, Anchor: #MJDTGMHC
- Both roadways are two-lane conventional type, Anchor: #SCKTHKPM
- Intersection is simple, basically 90 degree crossing or tee, Anchor: #KQHXQLID
- Highway directions are reasonably obvious with individual cardinal direction markers, and Anchor: #DKBLQGNN
- Minor road has mostly local traffic.
Figure 3-11 illustrates the application of a double-headed arrow under these circumstances.
Figure 3-11. Use of Double-Headed Arrow in Directional Assembly
Anchor: #i1003773Special Design for Wide Directional Arrow Auxiliary Sign
Where two route signs share the same direction, a special type of arrow sign may be used. The special arrow sign extends across the width of both route signs. An example of this extra wide arrow sign is shown in Figure 3-12.
Figure 3-12. Extra Wide Directional Arrow
Anchor: #i1003795Lane Designation Auxiliary Signs
Purpose: Lane Designation auxiliary signs are used to direct a motorist to the proper lane for making a turn or following a numbered route. A Lane Designation auxiliary sign is mounted below the route sign(s) to which it applies.
Lane Designation auxiliary signs are typically used in developed urban areas. They are only used when there are two or more through lanes in one direction. They may be used in a Junction Assembly (page 3-28) or as a separate assembly. Figure 3-13 illustrates Lane Designation auxiliary signs.
The Lane Designation assembly is normally erected in two consecutive blocks, usually the third and fourth blocks, in advance of the highway turn or junction with another highway.
Figure 3-13. Lane Designation Auxiliary Signs
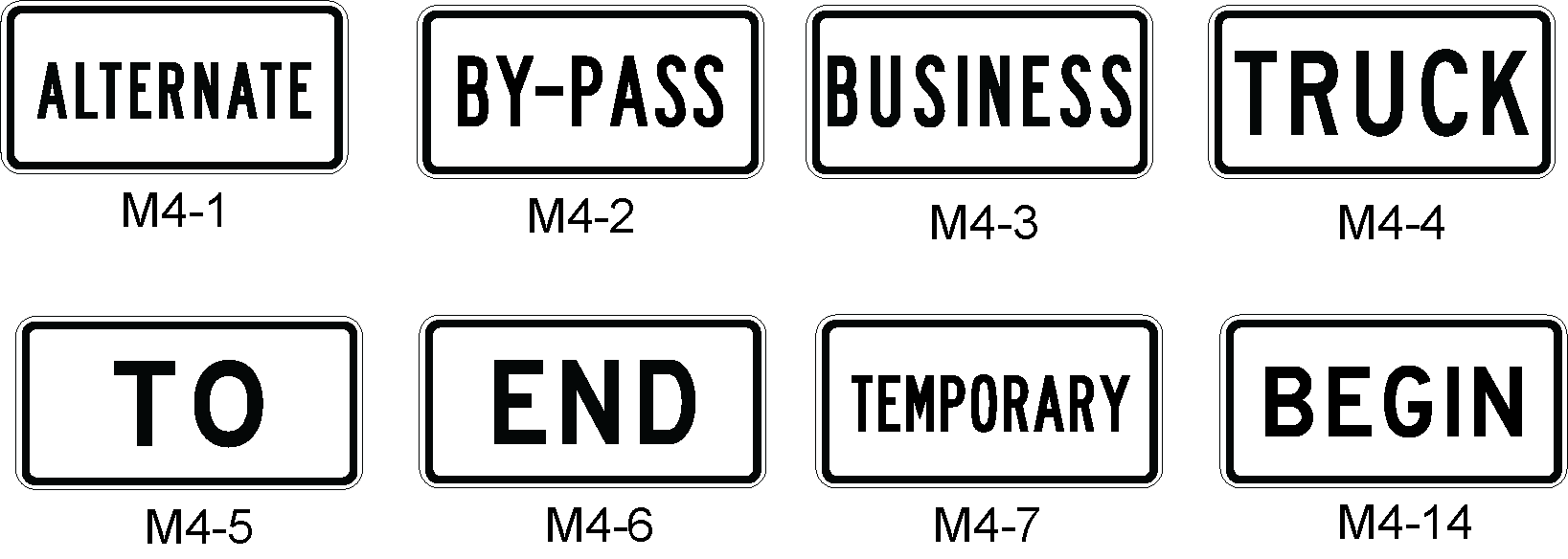
Anchor: #i1003825Other Auxiliary Signs (Texas MUTCD, Section 2D.16 to 2D.24)
There are several other types of auxiliary signs that may be used with route signs. They are described below and illustrated in Figure 3-14.
- Anchor: #RSVHIGMM
- ALTERNATE auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.17): The ALTERNATE auxiliary sign is used to identify a designated Alternate Highway. The ALTERNATE auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign. Anchor: #QLKEIEAP
- BY-PASS auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.18): The BY-PASS auxiliary sign is used to identify a route that branches from the numbered route through a city, bypasses a part of the city or congested area, and rejoins the numbered route beyond the city. The BY-PASS auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign. Anchor: #JTMQABQV
- BUSINESS auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.19): The BUSINESS auxiliary sign is used to identify a designated Business Highway. The BUSINESS auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign. Anchor: #QQNLJIWL
- TRUCK auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.20): The TRUCK auxiliary sign is used to designate an alternate route for trucks to avoid congested areas or areas that have height or weight limitations. The TRUCK auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign. TRUCK auxiliary signs are used as part of a Trailblazer Assembly. Anchor: #LNUFKWDP
- TO auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.21): The TO auxiliary sign is used as a trailblazer to indicate the route to a nearby highway that is not located at the current intersection or interchange. The TO auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign. TO auxiliary signs are used as part of a Trailblazer Assembly (page 3-33). Anchor: #RQCPDIRM
- END auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.22): The END auxiliary sign is used to inform the motorist that the designated route is terminating. The END auxiliary sign is mounted above the route sign or above a sign for an alternative route. Anchor: #WETXCKXK
- BEGIN auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.23): The BEGIN auxiliary sign is used to inform the motorist that the designated route is beginning. The BEGIN auxiliary sign is mounted above the first confirming assembly for a route that is beginning. Anchor: #WSFGGQKU
- TEMPORARY auxiliary sign (Texas MUTCD 2D.24): The TEMPORARY auxiliary sign is used for an interim period to designate a section of the highway that is not planned as a permanent route, but that connects completed portions of that route. The TEMPORARY auxiliary sign is mounted directly above the route sign, Cardinal Direction sign, or above a sign for an alternative route.
Figure 3-14. Other Auxiliary Signs