Chapter 9: Linked Route Segments
Anchor: #i1010975Section 1: Key Points to Know
Anchor: #i1010980Linked Route Defined
The mileage required to travel each designated highway route might include some route segments identified with different highway designations. These are Linked Route Segments and they:
- Consist of on-system or off-system roadways
- Interrupt the mileage and reference marker flow of the Signed Highway
- Are not part of the network length of the Signed Highway
- Are used strictly for determining the distance from origin for features occurring beyond the link segment.
Three Types of Links
There are three basic types of Linked Route Segments:
This chapter describes the differences among the three types of links and the input instructions.
Anchor: #i1011049Office of Responsibility
TPP is the Office of Primary Responsibility (OPR) for processing linked routes, which includes adding, updating, and deleting links from routes in TRM.
Click this link for your district’s TRM analyst.
Anchor: #i1011072Definitions
Ascending Marker Direction—Direction of travel in which the reference marker numbers increase.
Descending Marker Direction—Direction of travel in which the reference marker numbers decrease.
Interrupted Route—Secondary route of a linked route situation. Mileage and reference marker flow ends at the link and begins again past the end of the link.
Link Begin/End—Identifies the beginning or ending point of a linked route section. Valid values: B (beginning point of linking section) or E (ending point of linking section).
Link Reference Marker Group—Consists of the Link Reference Marker Number + Link Reference Marker Suffix + Link Reference Marker Displacement:
- Number—Official number posted on the signed highway route serving as a link for an interrupted signed highway route. Used together with the other components of the Link Reference Marker Group to locate the beginning or ending point of the link. Valid values: 0000 to 9998 (for Interstate Highways) or 0010 to 9998 (for non-interstate highways)
- Suffix—Posted suffix character, if any, for the Link Reference Marker Number on the signed highway route. Used together with the other components of the Link Reference Marker Group to locate the beginning or ending point of the link. Valid values: Blank (no suffix) or A thru Z.
- Sign—Symbol indicating the ascending or descending direction to the beginning or ending of a link from the Link Reference Marker Number. Valid values: + displacement in ascending reference marker direction or – displacement in descending reference marker direction
- Displacement—Distance in miles from a posted reference marker on the signed highway route to the beginning or ending of a link. Used together with the other components of the Reference Marker Group to locate data on the highway in TRM. Valid values: 00.000 to 99.999
Link Signed Highway Group—Consists of the Link Signed Highway System + Link Signed Highway Number + Link Signed Highway Suffix
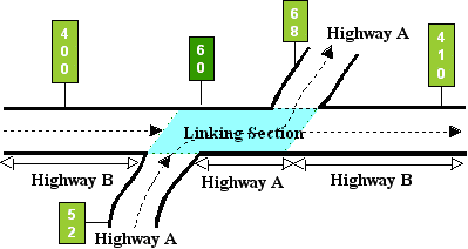
- Highway—Highest priority designated highway system for a segment of the highway network within a linking segment (see Figure 9‑1). All data and reference markers are tied to this route within the linking segment. This route serves as a link for an interrupted signed highway route:
-
Figure 9-1. Highway B is the “interrupted route”, input as the Signed Highway. Highway A is the “continuous route”, input as the Link Signed Highway. (The shaded area is the linked section for both routes.)
- Number—Identification number associated with the Link Signed Highway System serving as a link for an interrupted signed highway route. Valid values: 0001 – 9999, NASA, and OSR
- Suffix—Character appended to the Link Signed Highway Number to further partition the number or, in the case of business routes, to indicate geographical routing. Determine valid values by the Link Signed Highway System
Link Type Value and Notation—Character used to identify whether the linking section is a Concurrency, On-System, or Off-System linking section:
|
Value |
Link Type |
|---|---|
|
21 |
Concurrency |
|
22 |
On-System Link |
|
23 |
Off-System Link |
The Notation provides additional information about the link between segments of another highway.
Off-System Link—Created when a highway designation stops at a point on a given local road or street and starts again from another point on the same or different local road with a driveable connection between the two points.
On-System Link—Highway designation of one route stops at the intersection of another route and starts again from a second intersection with the same route creating an on-system link.
Primary Route—Used when referring to the continuous, uninterrupted Link Signed Highway route of the link situation.
Anchor: #i1011175Linked Route vs. Roadway Gap
Although linked route segments and roadway gaps both involve an interruption in data, learn to recognize the difference:
- Linked route segments have mileage associated with them. All affected routes use this mileage within the linked route segment to determine the overall route length and distance between reference markers before and after the link route segment
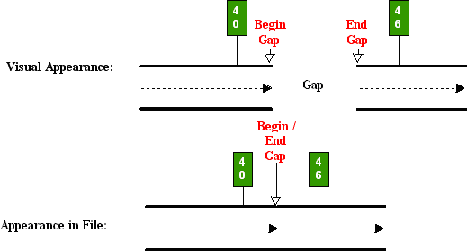
- Roadway Gaps do not have any mileage associated with them. Because the roadway gap is not driveable, there is no distance recorded between the beginning and ending of the gap. Figure 9‑2 below shows what a gap looks like on the road versus what it looks like in the file: The begin and end points are physically separated on the roadway, yet occupy the same space in the file:
-
Figure 9-2. How the TRM system “sees” a roadway gap.
Determining the Link Points
Determine the marker location points input for the link by characteristics within the Signed and Linking Signed Highways. Remember:
- the route input as the Signed Highway is always the route interrupted by another on- or off-system road
- the route input as the Linking Signed Highway is always the route which remains continuous with no interruption in data or reference markers.
The Signed Highway/Secondary Route
The Signed Highway (secondary route) includes the Signed Highway and From Reference Marker Group. You need only one marker location point, which is the location of:
- A roadway gap
- The beginning of the route (concurrencies only)
- The ending of the route (concurrencies only).
The Linking Signed Highway/Primary Route
The Linking Signed Highway (primary route) includes the Link Signed Highway and both Link From and To Reference Marker Groups. The direction of travel of the Linking Signed Highway determines which marker is input as the From Marker location and which is input as the To Marker location.
Anchor: #i1011266Ascending Marker Direction
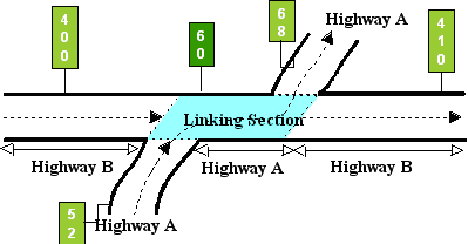
Example 1: In Figure 9‑3, Highway B travels west to east while Highway A travels south to north (or west to east). Because A (the Linking Signed Highway) travels in the same direction as B (the Signed Highway), input the markers for A in ascending marker direction:
Figure 9-3. Segment of Highway A between segments of Highway B is the link, ascending marker direction.
If the direction of travel of the Linking Signed Highway is the same as the Interrupted Signed Highway, input the From and To marker location points for the Link Signed Highway in ascending marker direction.
Anchor: #i1011291Descending Marker Direction
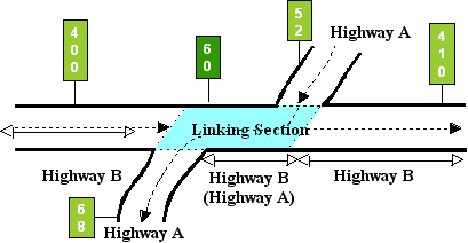
Example 2: In Figure 9‑4, Highway B travels west to east while Highway A travels north to south. Because A (the Linking Signed Highway) travels in the opposite direction of B (the Signed Highway), input the markers for A in descending marker direction:
Figure 9-4. Segment of Highway A between segments of Highway B is the link, descending marker direction.
If the direction of travel of the Linking Signed Highway is different from the Interrupted Signed Highway, input the From and To marker location points for the Link Signed Highway in descending marker direction.